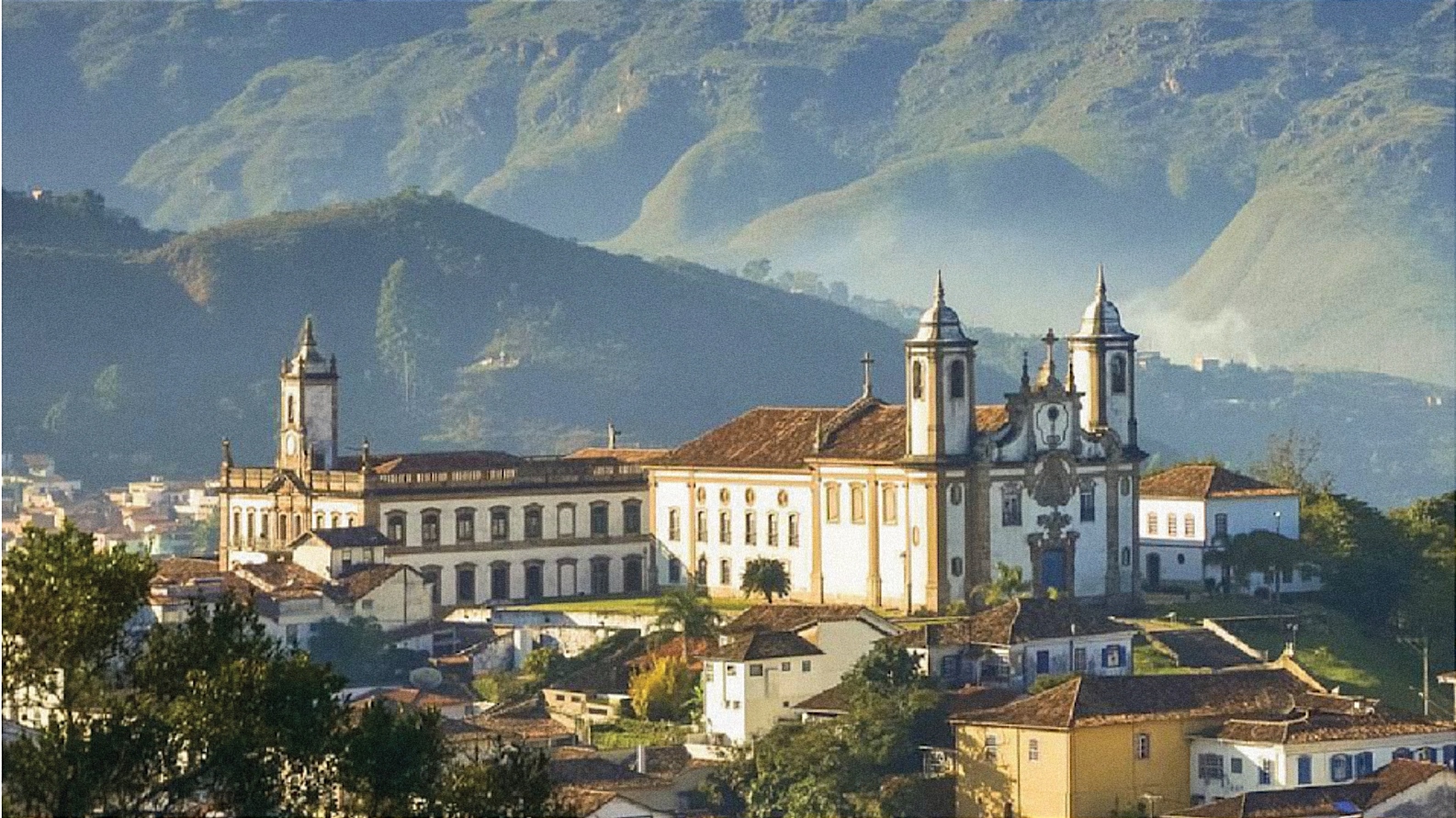
The city of Ouro Preto
Born from explorer Antônio Dias’s discovery of “ouro preto” (black gold) in the Tripuí riverbed in the 17th century, the history of the city could be conflated with Brazil’s. Ouro Preto enjoyed its gilded age during the Ciclo do Ouro , when it was the stage for the Inconfidência Mineira, a separatist movement led by Tiradentes and motivated by the Portuguese crown’s high taxation of gold.
The wealth of the region, which produced majestic churches, was also the matter for intrigue and the target of many criminal schemes—like the bandits led by Vira-saia who sometimes assaulted cattle dealers carrying gold en route to Portugal.
In an attempt to prevent these attacks, they opened the Estrada Real, or Royal Road, connecting Ouro Preto to the cities of Paraty and Rio de Janeiro. Constructed on the backs of black slaves laboring in the mines, the city still has strong traces of African culture—despite having being marginalized for years— evident in Capoeira, Congados, and religious syncretism. Chico Rei is considered a hero of the black resistance in Ouro Preto, since, after buying his freedom, he became the owner of his own gold mine, known as the Mina do Chico Rei.
The decline of Ouro Preto’s mines, at the end of the 18th Century, led much of the population to abandon the city. This migration, on the other hand, led to the preservation of its historical center, the largest example of Baroque architecture in the world, and a World Heritage sight since 1980. Especially noteworthy are the works of Aleijadinho and Master Ataíde.
Inspiration for poets and artists, for mysterious legends and stories that have persisted generation after generation among its inhabitants, Ouro Preto is an icon survived in Tomás Antônio Gonzaga’s poetry, in Guignard’s canvases and in the imagination of all who have the chance to visit.
Our state is known for its typical cuisine, and no visitor of Ouro Preto can resist a warm Pão de Queijo (cheese bread), Frango com Ora-pro-nobis (a traditional chicken dish) cooked in a stone pot, or a Romeu e Julieta (also known as goiabada com queijo or a guava preserve paired with cheese).
Ouro Preto is also recognized by its intense cultural life with an extensive calendar of events throughout the course of the year. The Fundação de Arte de Ouro Preto, the Orchestra Ouro Preto and the Instituto Candonguêro are important organizations that promote culture in the city, developing various projects together with the artists and the community.
Buildings
Set in a total area of 150.7 thousand m², since its very inception and even before, UFOP has been overcoming challenges related to investment and physical adaptation. These challenges have been especially in the cities and Historical Heritage sites of Ouro Preto and Mariana. UFOP was founded in 1969 by uniting the centenary School of Pharmacy (1839) and School of Mines (1876) in their former buildings, located in the Historic Center of Ouro Preto. Initially, given the needs of the programs, restorations and expansions were made to adapt those buildings to academic use. However, it was soon realized that, either due to the historical heritage constraints and restrictions, or the physical limitations of the buildings, it was no longer possible to meet the demands of the program expansions and the university itself. From that moment the Morro do Cruzeiro Campus was created and, years later, the ones in Mariana and João Monlevade.
Academic units in Ouro Preto
| The Center of Open and Distance Education (CEAD): is an academic unity that aims at the consolidation and improvement of distance learning, offering undergraduate, graduate and extension programs through distance education (EAD), as well as support to other units for the accomplishment of academic activities through this modality. It was created in 2003, consolidating an experience that began in the late 1990s. | |
| The School of Physical Education (EEF): offers bachelor degrees in Physical Education, also offering courses in several programs throughout the University and developing research and extension projects in this area. | |
| The School of Law, Tourism and Museology (EDTM): is an academic unity formed by the union of three departments, Law Department (DEDIR), Tourism Department (DETUR) and Museology (DEMUL), which support and develop activities and projects in these areas of knowledge. | |
| The School of Pharmacy (EFAR): was founded in 1839, being the first in Latin America in this field. It currently offers undergraduate programs in Clinical Analysis and Pharmaceutical Industry, specialization programs in Clinical Cytology and Clinical Analysis and masters degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences. | |
| The School of Mines (EM): idealized by Dom Pedro II and founded by Claude Henri Gorceix in October 12, 1876, it was the first in the country in geological, metallurgical and mining studies. It currently offers undergraduate and graduate programs, activities and projects in several areas of Engineering and Architecture. | |
| The School of Medicine (EMED): founded in 2012, it offers programs and activities in the health area, especially in the training of doctors. The unit is also responsible for the Medical Residence Graduation Program in three specialization areas: Medical Clinic, General Surgery and Family and Community Medicine. | |
| The School of Nutrition (ENUT): the Nutrition Program started in 1978, initially as part of the School of Pharmacy. It acquired autonomy in March 1982 with the creation of an independent Program, in parallel with the inauguration of its own installations. Currently the unit develops activities and projects connected to nutrition and food sciences. | |
| The Institute of Exact and Biological Sciences (ICEB): founded in 1982, it was the first academic unit installed exclusively in Morro do Cruzeiro Campus. It was created with the intention to unite the basic cycles of the Pharmacy, Nutrition and Engineering Programs. It currently offers undergraduate and bachelor’s degrees, as well as basic cycle courses to other university programs. | |
| The Institute of Philosophy, Arts and Culture (IFAC): with the growing awareness and interest from the community in the area of Arts, it was created in 1994. It includes the Philosophy, Arts and Music Programs, also offering graduate programs in Philosophy and Dramatic Arts. |